Using gold in the manufacturing process of computers has been a thing for a while now. The reason for using gold is not because it looks nice, but because gold is a great conductor of electricity that is unlikely to corrode. The karat weight of gold used in computers usually ranges from 10-24 karats. The most common karat weight for computer parts is 18 karat, which is about 75% pure gold. 24 karat gold is 100% pure gold, but it is too soft to be used in most computer parts. Here’s how much gold is in major computer parts.
What Karat Gold Is Used In Computers?
The purity of the gold determines how karat it is and this can affect how it functions in electronic devices, so if you’re wondering what karat gold is used in computers, it depends. 24 karat gold is too soft to be used in most electronics, so it is often used for decorative purposes.
Then, in computing, gold is mostly used as a connector on printed circuit boards and for contacts that relay electrical signals. The connectors and contacts must be very reliable and durable in order to function correctly, which is why higher karat golds are often used in these applications.
For example, 18 karat gold has a lower resistance to corrosion than 10 karat gold, making it a better choice for contacts that will be exposed to the environment. In addition, 18 karat gold contains less copper than 14 karat gold, so it has a lower melting point and is less likely to warp or deform when soldered to a circuit board.
10 karat gold is often used in less demanding applications where lower cost is more important than performance. In the end, it’s all about finding the right balance of properties for each application.
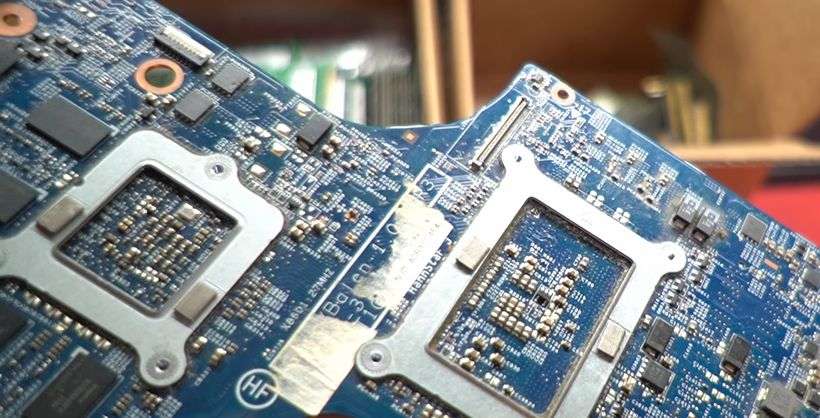
How Much Gold Is In A Motherboard?
Generally, a small laptop motherboard contains about 0.006 grams of gold, while a full-size desktop motherboard contains about 0.2 grams of gold. Some high-end gaming motherboards contain even more gold.
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board found in computers and other electronic devices. Boards come in a variety of sizes, from about 6 by 8 inches (15 cm × 20 cm) for a small laptop to 11 by 17 inches (28 cm × 43 cm) for a full-size tower desktop. The amount of gold in a motherboard depends on its size and the number of functions it performs.
Most of the gold in a motherboard is used for electrical contacts and connectors. A small amount is also used in plating the surface of connector pins and other metal surfaces to prevent corrosion.
How Much Gold Is In A Computer Processor?
The amount of gold in a computer processor depends on its size and the number of transistors it contains. A small smartphone processor contains about 0.025 grams of gold, while a high-end server processor contains about 0.5 grams of gold.
A computer processor is the part of the computer that performs the calculations and controls the other parts of the computer. A processor is made up of millions of transistors, and a little bit of gold is used to connect each transistor to the next one.
Processors come in a variety of sizes, from about 1 square inch (6.5 cm²) for a small smartphone processor to about 12 square inches (77 cm²) for a high-end server processor.
Is There Gold In Computer Monitors?
Gold is used in a variety of different ways in computer monitors. In some cases, it is used as a conductor to help move the electrons that create the image on the screen. In other cases, it may be used as a sealant or adhesive to hold different components together.
The purity of gold used in these applications can vary depending on the needs of the manufacturer. Most computer monitors use gold with a karat rating of 18.
Also, a thin layer of gold is sometimes applied to the exterior of computer monitors to give them a more luxurious appearance. This gold plating usually has a karat rating of between 10 and 14.
Is It Profitable To Recycle Gold From Electronic Devices?
When some people hear for the first time that there’s gold in computers their first thought is to harvest it. But is this a profitable idea? The answer to that question is not simple. It depends on a lot of factors, including the karat of gold in the device, how much gold is in the device, and what the market conditions are for gold.
This question has become more relevant lately because of the growth in sales of electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. A lot of these devices contain gold, not only in the circuit boards and connectors, but also in the plating on the buttons, keys, and casings. The amount of gold in a device ranges from a few milligrams to a few grams.
The high price of gold has made recycling it from electronic devices more attractive. For example, if the gold content of a device is 1 gram and the market price for gold is $1,000 per ounce, then the recycled gold would be worth $10. If the market price for gold were to rise to $2,000 per ounce and keep in mind it’s currently already at $1,970, the recycled gold would be worth $20.
But there are costs associated with recovering the gold from electronic devices. These costs include the cost of dismantling the device, the cost of extracting the gold, and the cost of refining the gold. So, if these costs are greater than the value of the recycled gold, it may not be profitable to recycle it.
The karat of gold is also a factor in whether or not it is profitable to recycle it. The higher the karat, the more valuable the gold. For example, as you remember 24-karat gold is considered to be pure gold, while 10-karat gold is only 10% pure. So, if a device contains mostly 10-karat gold, it may not be worth the cost to recycle it, because the gold would only be worth 10% of what it would be if it were pure gold.
Final words
Gold is a valuable resource that is used in many different ways in computers. Its non-corrosive and electricity conducting properties make it an ideal material for use in electrical contacts, connectors, and other components. The purity of gold used in electronics depends on the part of the device. In the long run, using gold in computers can be more cost-effective than using other metals.






